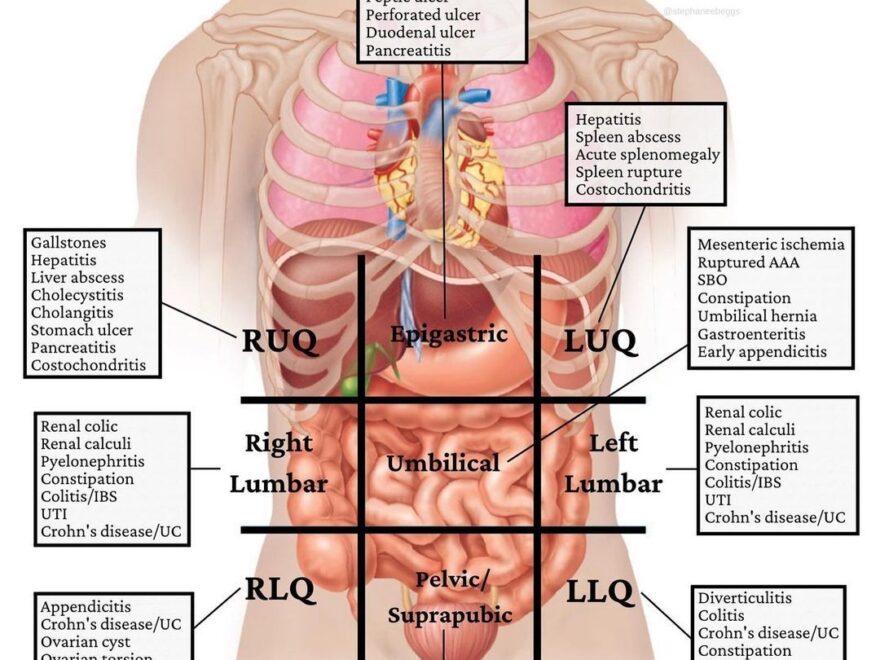
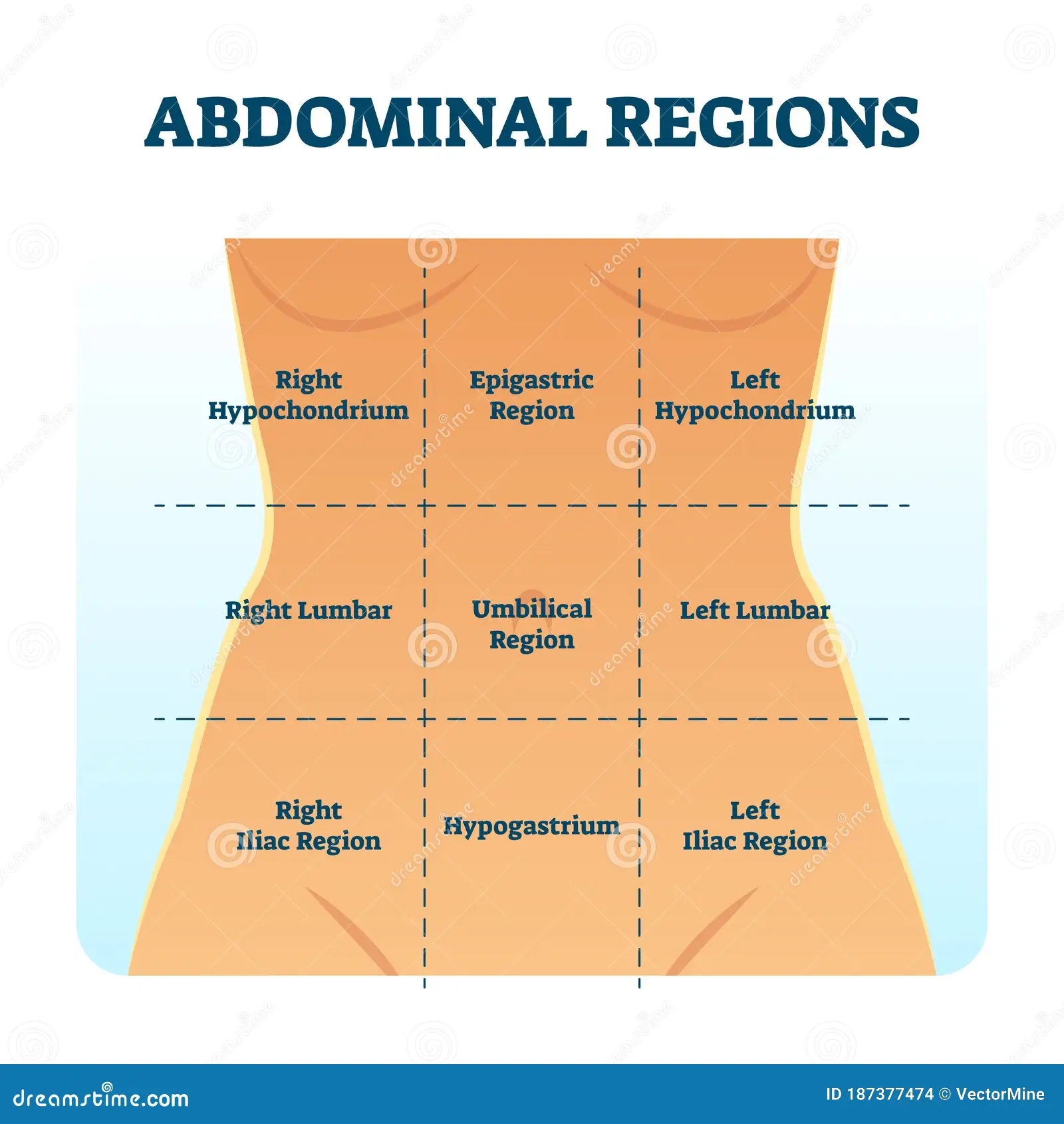
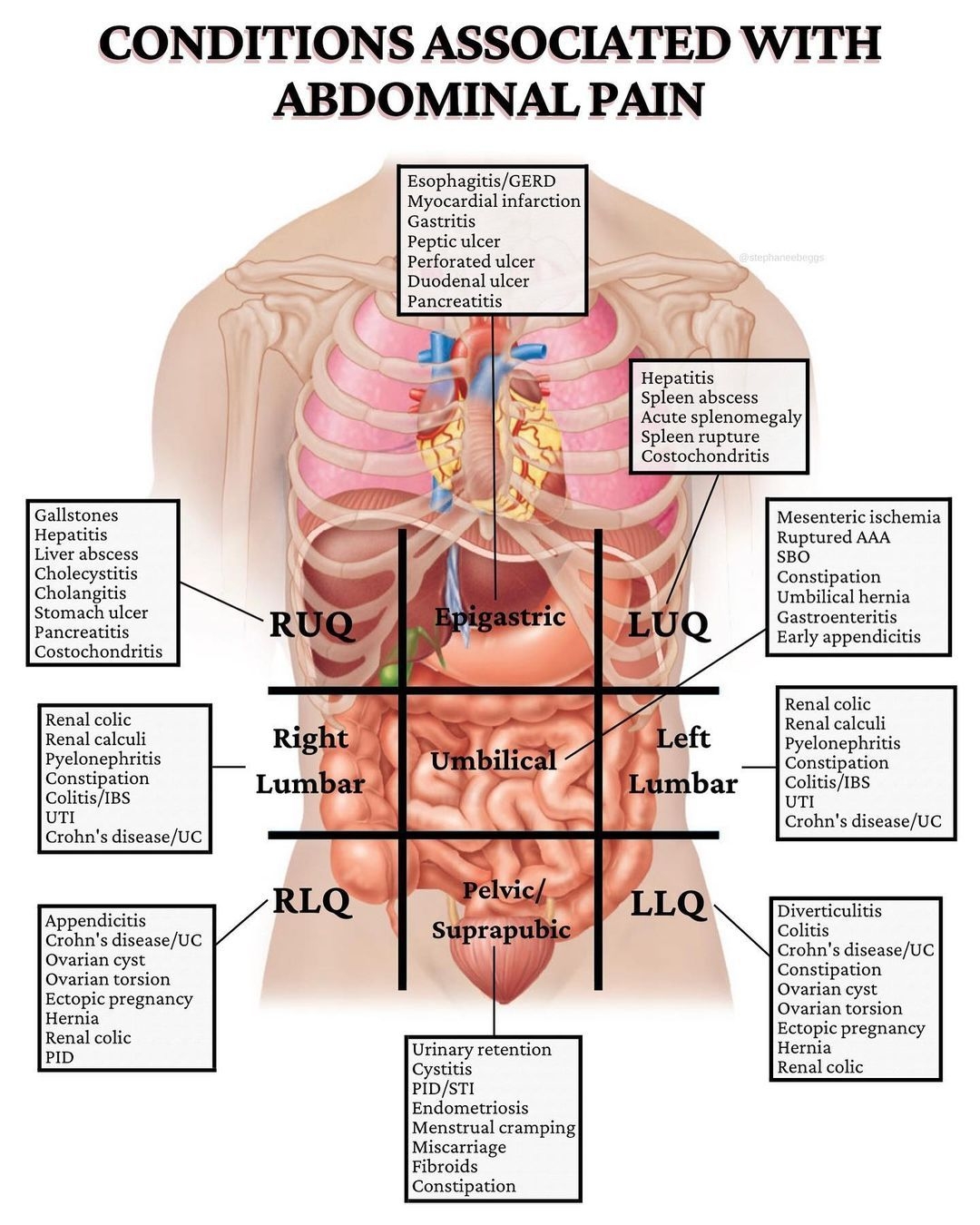
Have you ever wondered how a 4 quadrant graph works and why it’s essential in various fields? Understanding the anatomy of a 4 quadrant graph can help you interpret data more effectively and make informed decisions.
From business analysis to personal finance management, 4 quadrant graphs are versatile tools that visually represent relationships between two variables. By dividing the graph into four quadrants, you can quickly identify trends, patterns, and correlations.
4 Quadrant Graph Anatomy
4 Quadrant Graph Anatomy
The x-axis and y-axis intersect at the origin point (0,0) in the center of the graph. The x-axis represents one variable, while the y-axis represents the other variable. Each axis is divided into positive and negative values, creating four quadrants.
The first quadrant (top right) represents positive values for both variables, indicating a positive correlation. The second quadrant (top left) has negative x-values and positive y-values, showing an inverse relationship. The third quadrant (bottom left) has negative values for both variables, indicating a negative correlation.
Lastly, the fourth quadrant (bottom right) has positive x-values and negative y-values, showing another type of inverse relationship. Understanding the anatomy of a 4 quadrant graph allows you to interpret data accurately and draw meaningful conclusions from your analysis.
Whether you’re analyzing sales data, tracking market trends, or evaluating personal goals, 4 quadrant graphs can provide valuable insights into relationships between different variables. By mastering the anatomy of a 4 quadrant graph, you can enhance your data visualization skills and make better-informed decisions in any field.
Abdominal Quadrant Regions Scheme As Stomach Division Vector Illustration Stock Vector Illustration Of Graph Educational 187377474
Four Abdominal Quadrants And Nine Abdominal Regions