Are you looking to understand the concept of a 4 quadrant graph with numbers? Well, look no further! This article will break it down for you in a simple and easy-to-understand way.
When it comes to a 4 quadrant graph with numbers, it’s all about visualizing data in a clear and organized manner. Each quadrant represents different combinations of positive and negative numbers, making it easier to analyze and interpret information.
4 Quadrant Graph With Numbers
Understanding the Basics of a 4 Quadrant Graph With Numbers
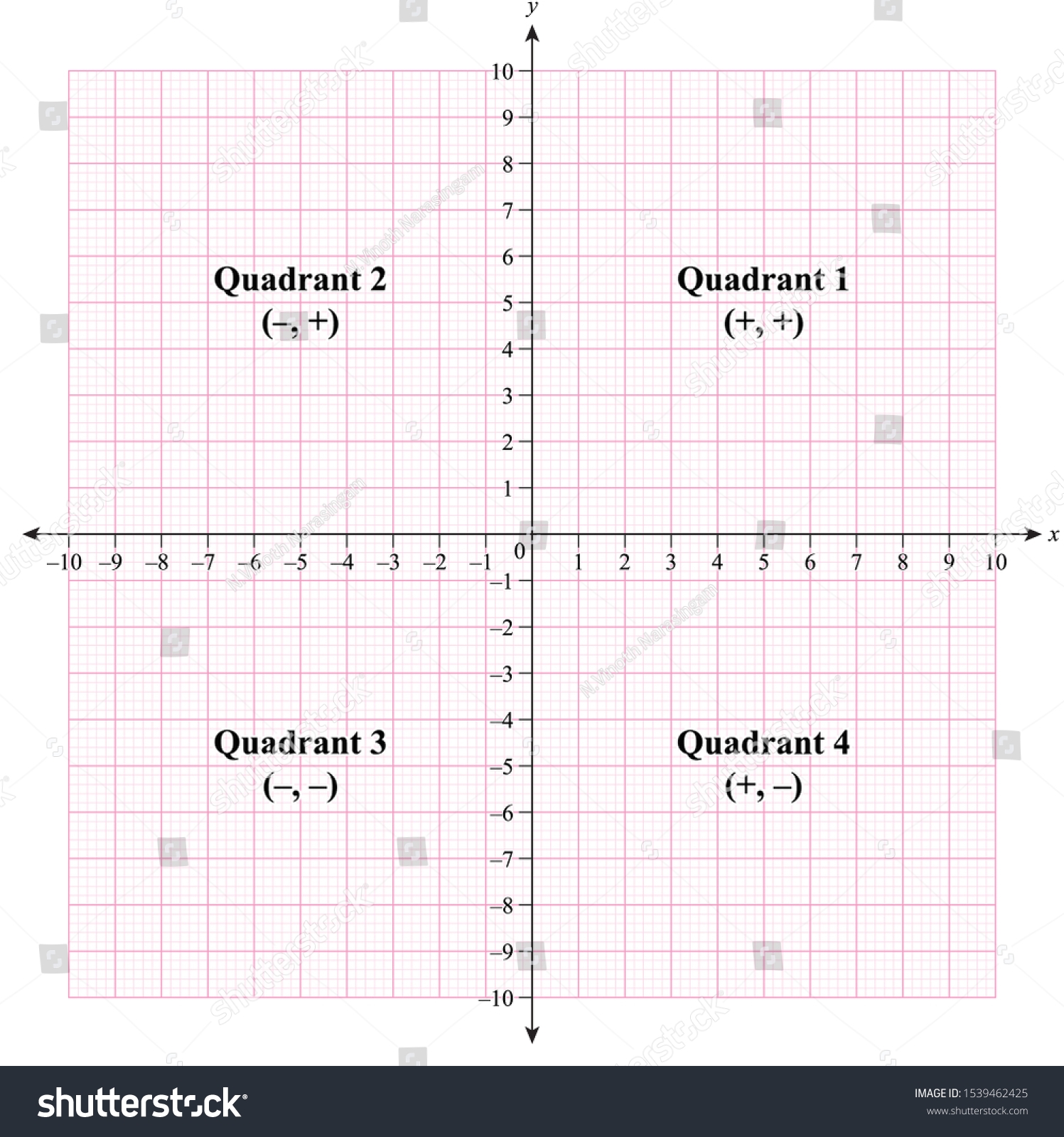
In a 4 quadrant graph, the x-axis represents positive and negative numbers horizontally, while the y-axis represents positive and negative numbers vertically. This creates four quadrants: Quadrant I, Quadrant II, Quadrant III, and Quadrant IV.
Quadrant I contains positive numbers for both x and y axes, Quadrant II contains negative x and positive y numbers, Quadrant III contains negative numbers for both x and y axes, and Quadrant IV contains positive x and negative y numbers.
By using a 4 quadrant graph with numbers, you can easily plot data points and see patterns or trends that may not be as obvious in a simple table or list format. This visual representation can help you make informed decisions based on the data at hand.
Whether you’re a student learning about graphing, a business professional analyzing market trends, or just someone curious about numbers, understanding a 4 quadrant graph with numbers can be a valuable skill to have in your toolkit.
So, next time you come across a 4 quadrant graph with numbers, don’t be intimidated! Remember that it’s just a way to organize and interpret data visually. Take your time to understand each quadrant and how they relate to the numbers you’re working with.
Now that you have a better grasp of what a 4 quadrant graph with numbers is all about, you can start applying this knowledge to your own projects or studies. Happy graphing!
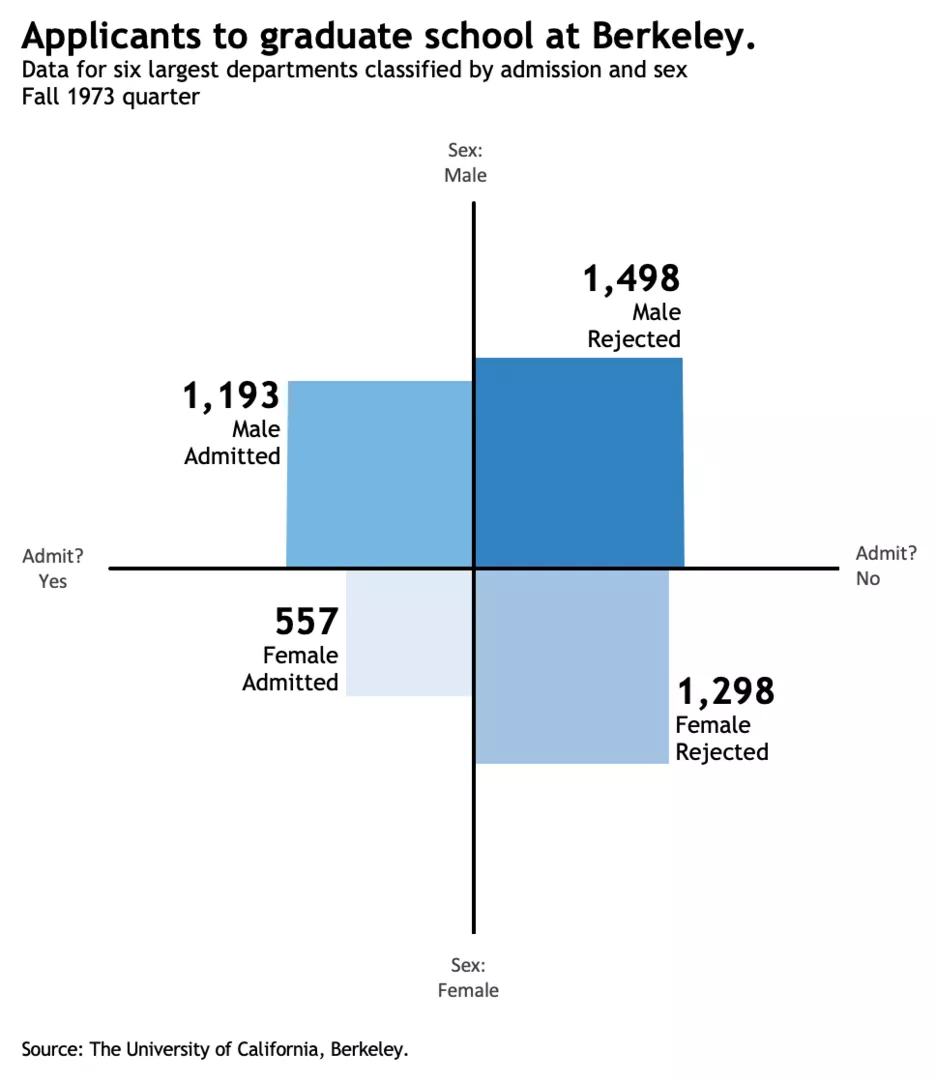
How To Create A Fourfold Chart In Excel
Ordered Pairs On A Coordinate Plane