Understanding the 4 quadrants of a graph can be a game-changer when it comes to interpreting data. These quadrants can help you make sense of information and draw valuable insights from it.
Whether you’re a student working on math homework or a business professional analyzing sales figures, knowing how to navigate the 4 quadrants can make your life a whole lot easier.
4 Quadrants Of Graph
The 4 Quadrants of Graph
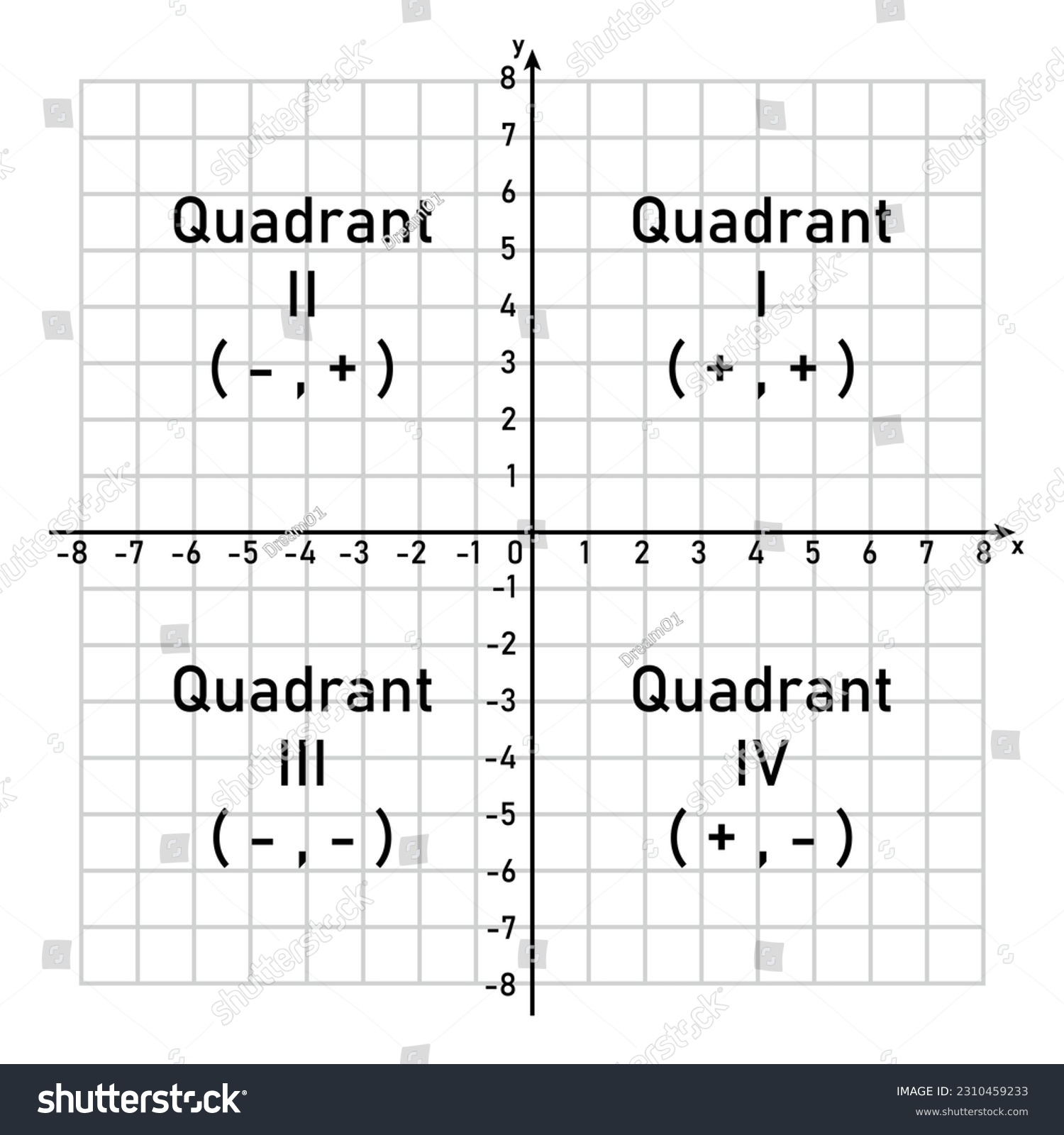
When you look at a graph, you’ll notice that it’s divided into four sections, known as quadrants. These quadrants are labeled with Roman numerals: I, II, III, and IV. Each quadrant has its own unique characteristics and significance.
Quadrant I is in the upper right corner and represents positive values for both the x and y axes. Quadrant II is in the upper left corner and has negative x values but positive y values. Quadrant III is in the lower left corner and has negative values for both x and y. Quadrant IV is in the lower right corner and represents positive x values but negative y values.
By understanding which quadrant a point falls in on a graph, you can quickly determine its coordinates and interpret its meaning. This can help you identify trends, patterns, and relationships in your data that may not be immediately apparent.
Next time you come across a graph, take a moment to identify the 4 quadrants and see how they can help you make sense of the information presented. You’ll be surprised at how much easier it is to analyze data once you understand the significance of each quadrant.
So, the next time you’re faced with a graph, don’t be intimidated by all those lines and numbers. Remember the 4 quadrants and how they can help you unlock the secrets hidden within the data. Happy graphing!
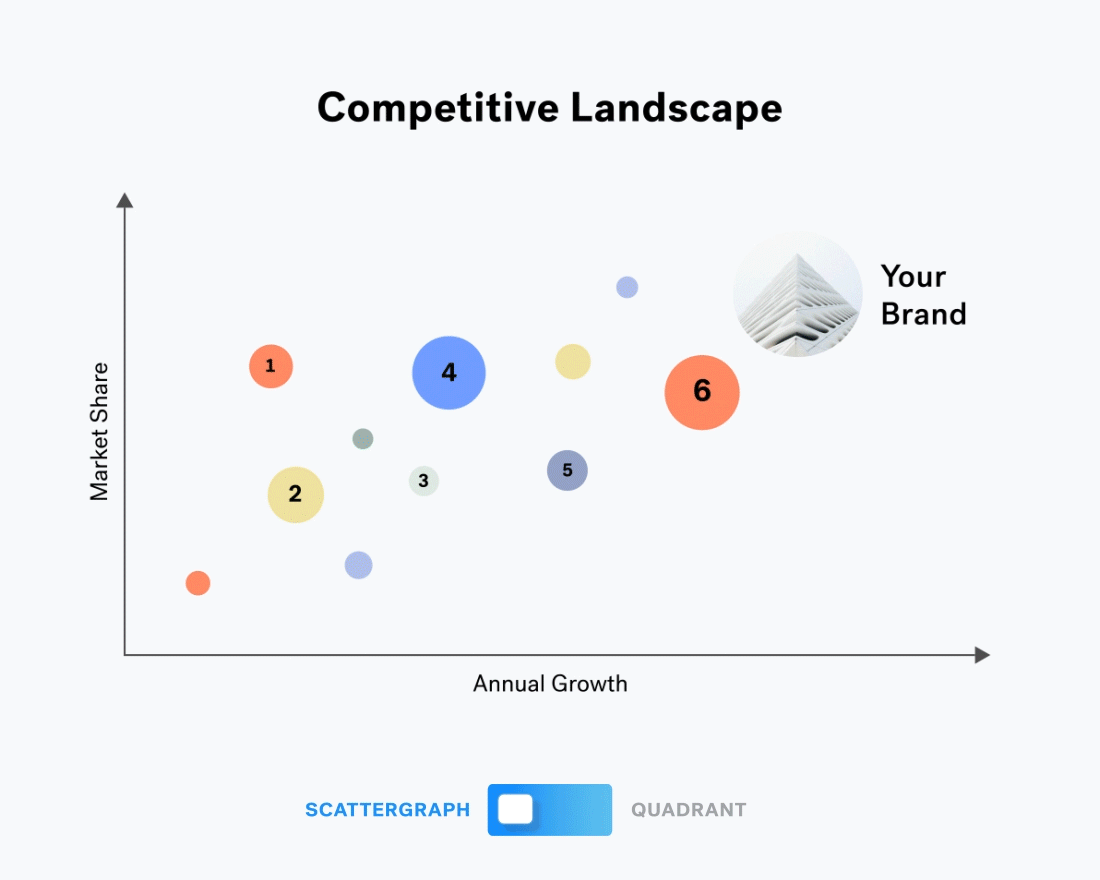
A Data Visualization Duel Scattergraph Vs Quadrant The Beautiful Blog
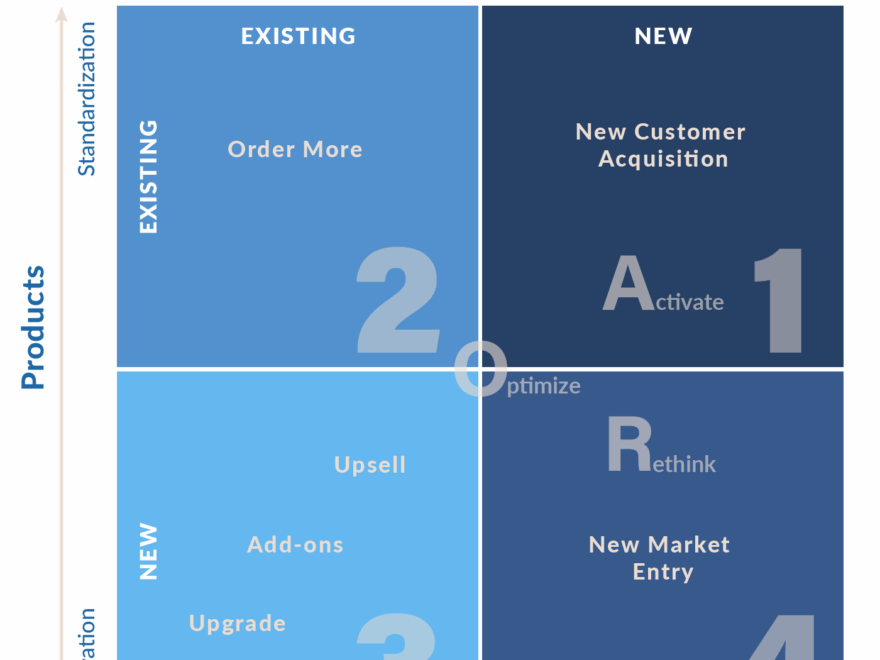
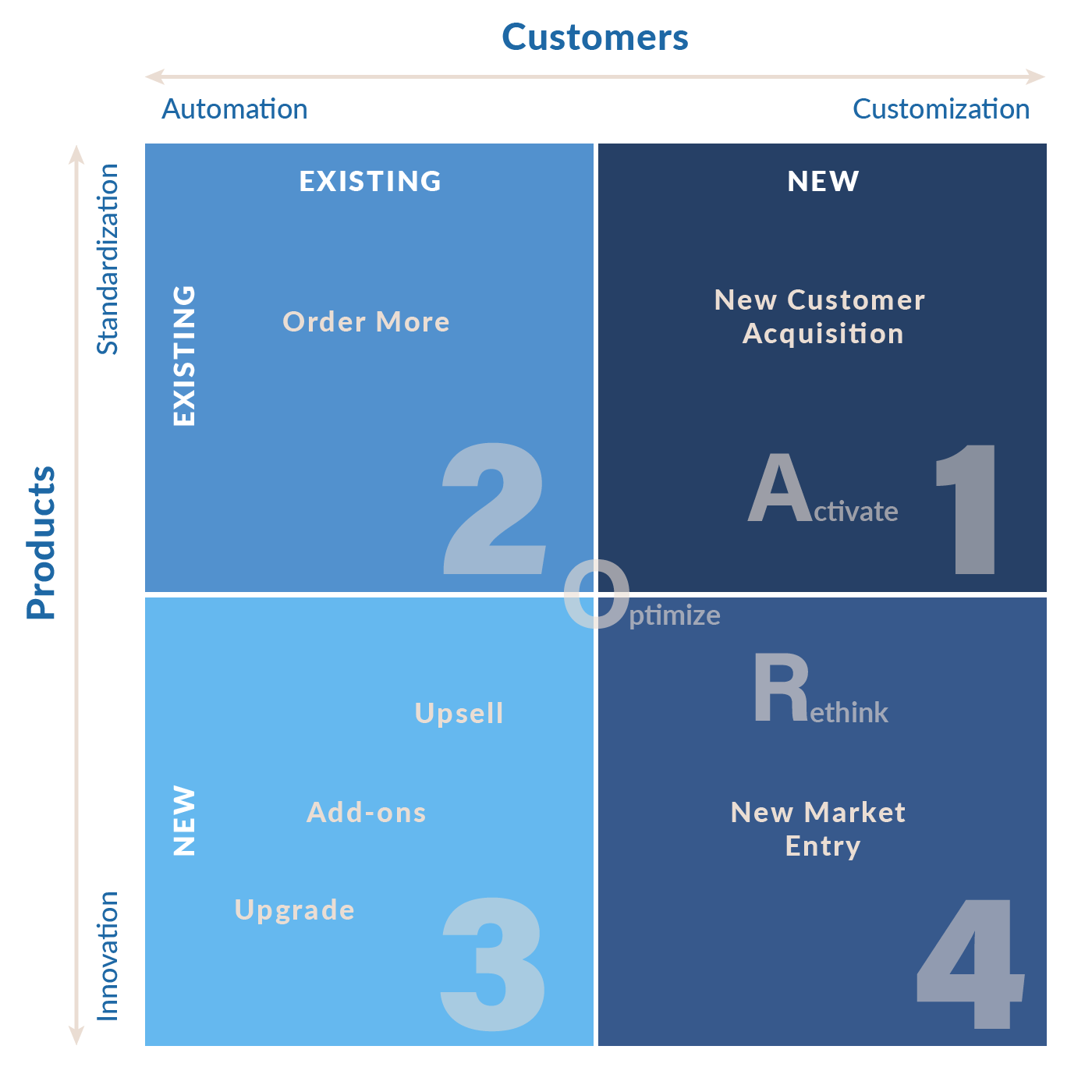
The Four Quadrants Model Of High Growth SOMAmetrics