Graphs are an essential tool in various fields, from business to science. One commonly used type of graph is the four quadrants graph, which helps visualize data in a clear and organized manner.
Understanding the anatomy of a four quadrants graph is crucial for interpreting and analyzing data effectively. By grasping the key components of this graph, you can unlock valuable insights and make informed decisions based on the information presented.
Four Quadrants Graph Anatomy
Four Quadrants Graph Anatomy
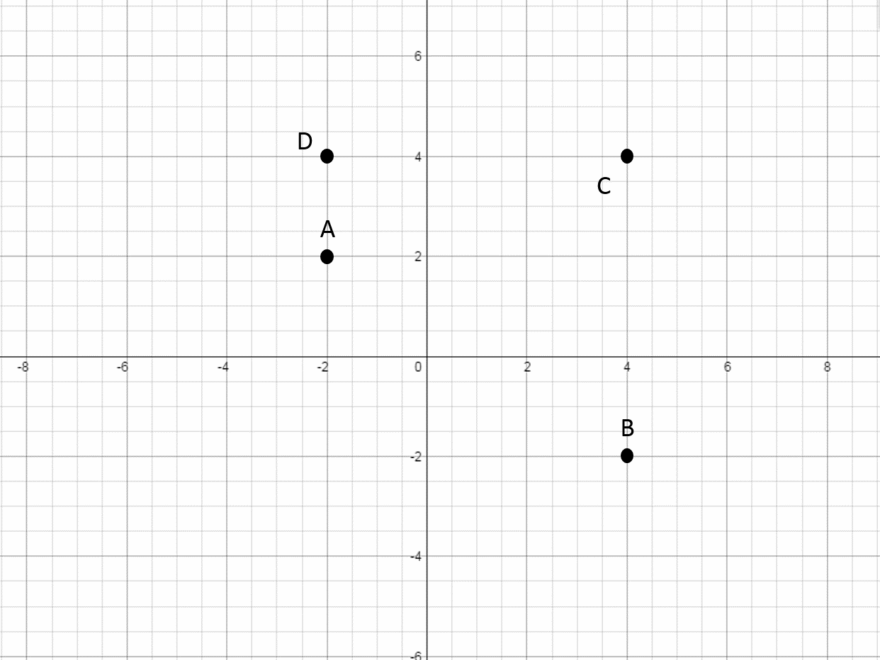
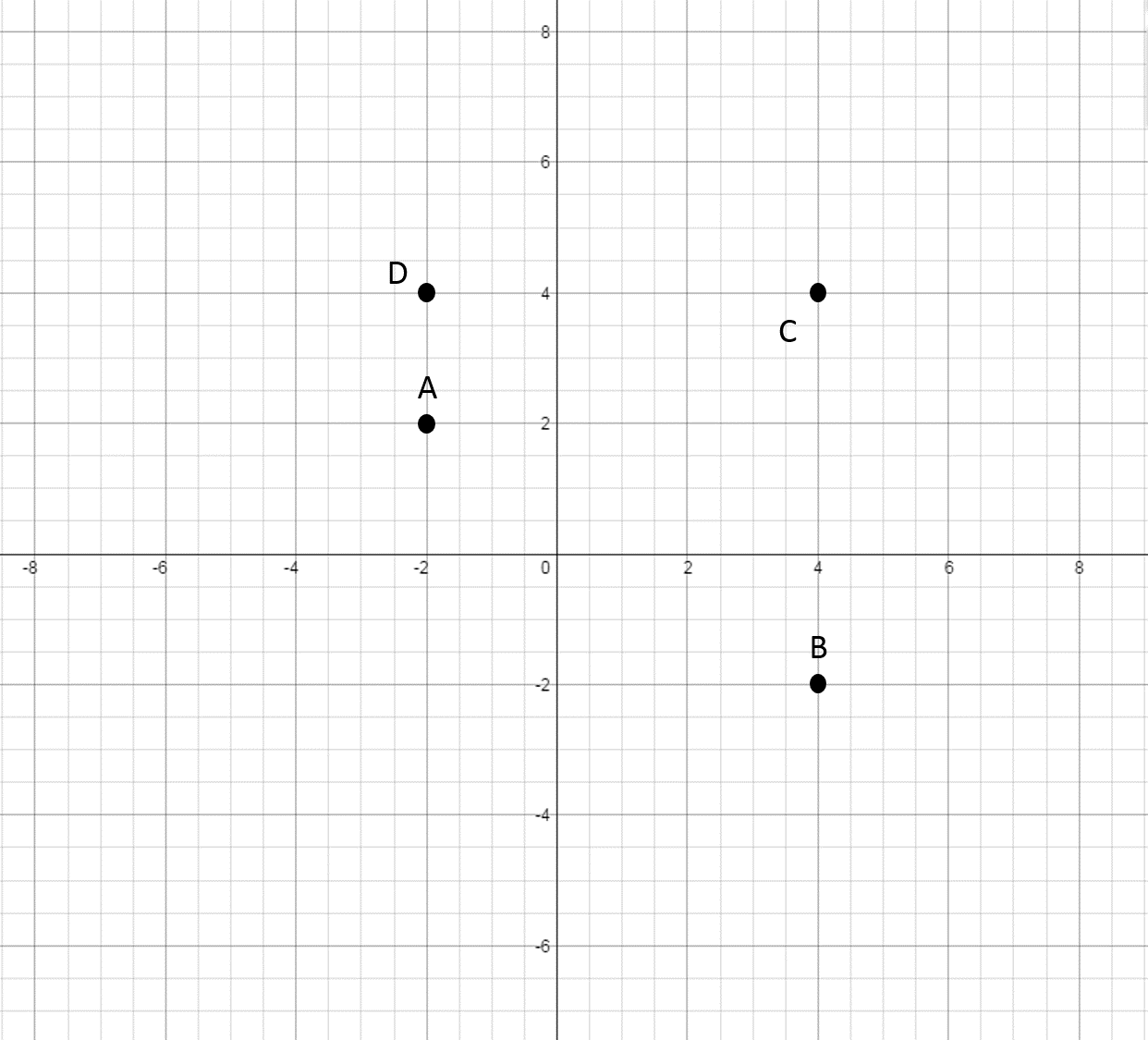
The four quadrants graph consists of four sections, each representing a different category or variable. The x-axis and y-axis intersect at the center, creating four distinct quadrants that allow for comparison and contrast between data points.
Typically, the horizontal axis (x-axis) represents one variable, while the vertical axis (y-axis) represents another variable. The intersection point of these axes serves as the origin, with positive and negative values extending outwards into each quadrant.
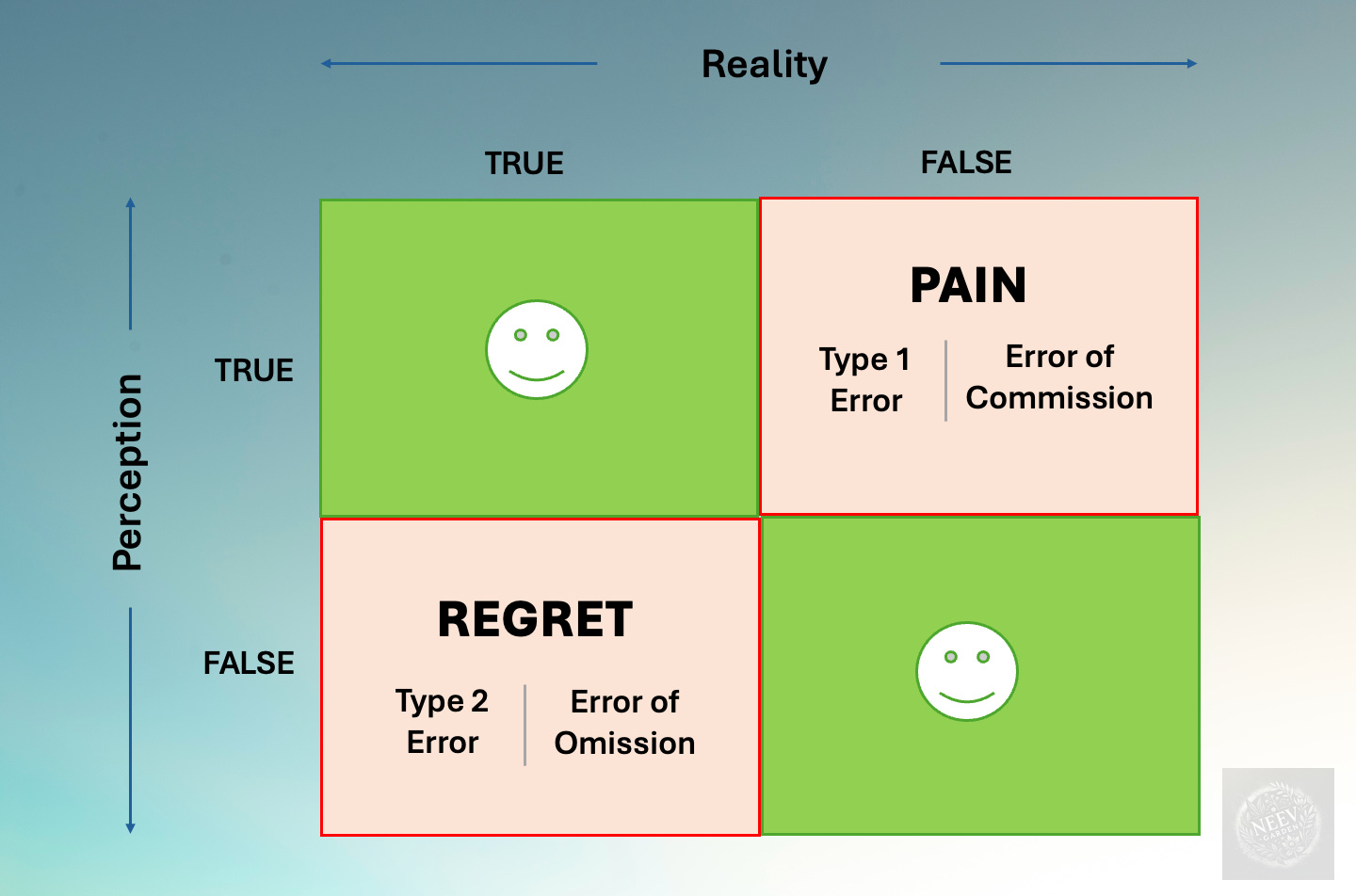
In a four quadrants graph, data points are plotted based on their corresponding values on the x and y axes. Each quadrant may have its unique significance, such as indicating trends, correlations, or outliers within the dataset being analyzed.
By incorporating labels, titles, and a legend, you can enhance the clarity and readability of a four quadrants graph. These additional elements provide context and guidance for interpreting the information presented, making it easier for viewers to understand the data at a glance.
In conclusion, mastering the anatomy of a four quadrants graph can empower you to extract valuable insights from your data and communicate findings effectively. By familiarizing yourself with the key components of this graph, you can leverage its visual representation to make informed decisions and drive meaningful outcomes in your work or research.
Coordinate Plane Poster For Classroom Etsy
How To Graph An Ordered Pair Algebra 1