Political science students often come across the term “4 Quadrants Graph” in their studies. This tool is commonly used to analyze and categorize political ideologies based on their views on economic and social issues.
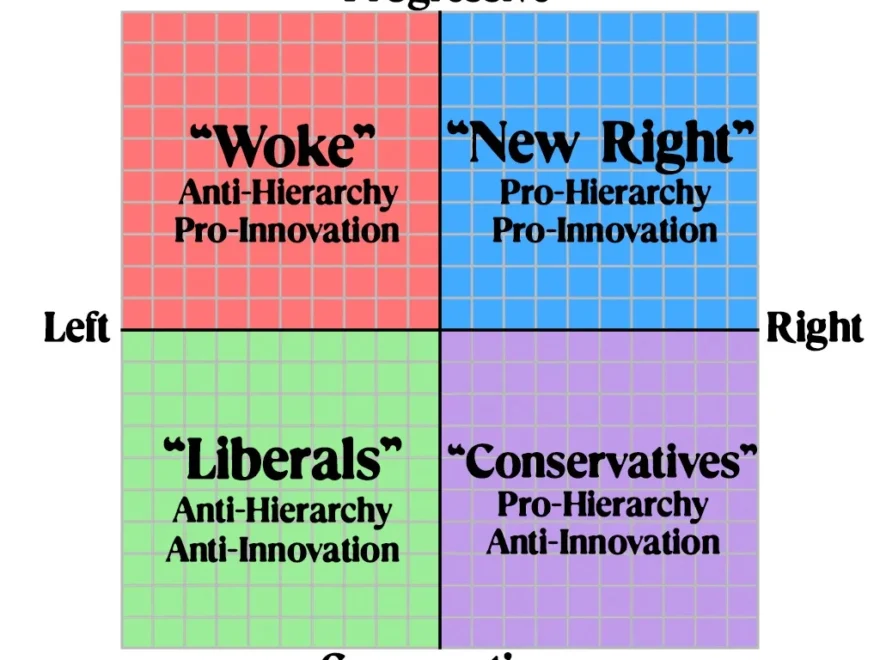
The 4 Quadrants Graph in political science divides political ideologies into four main categories: authoritarian right, libertarian right, authoritarian left, and libertarian left. Each quadrant represents a different combination of views on social and economic policies.
4 Quadrants Graph Political Science
Understanding the 4 Quadrants Graph Political Science
Authoritarian right ideologies, such as fascism, believe in strict social control and limited economic freedom. Libertarian right ideologies, like classical liberalism, prioritize economic freedom and limited government intervention.
On the other hand, authoritarian left ideologies, such as communism, advocate for strong government control over both social and economic aspects. Libertarian left ideologies, like anarchism, reject both government interference in social and economic matters.
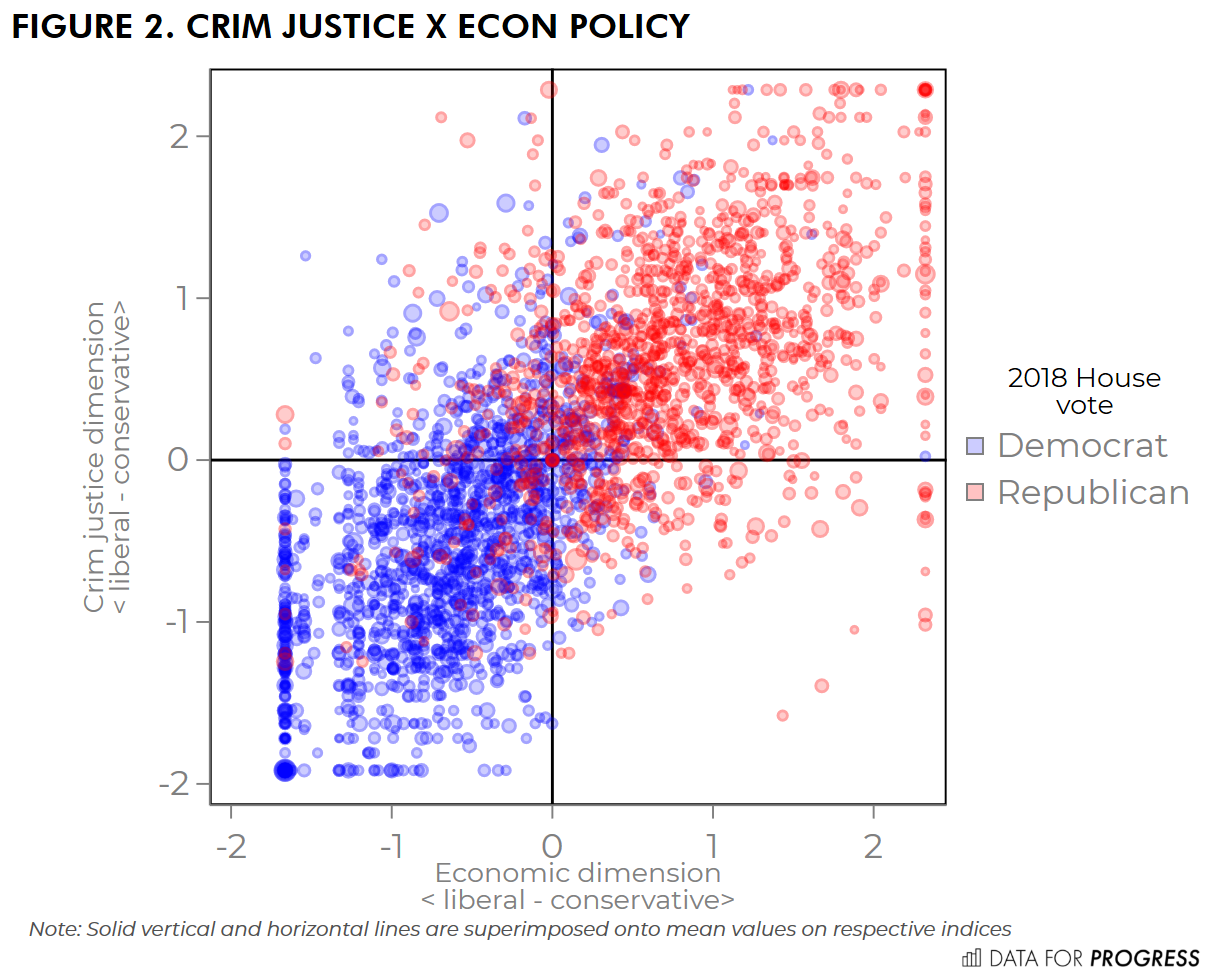
By using the 4 Quadrants Graph, political scientists can visually map out where different political ideologies fall on the spectrum of social and economic beliefs. This tool helps students and researchers compare and contrast various ideologies to better understand their differences and similarities.
Overall, the 4 Quadrants Graph in political science is a valuable tool for analyzing and categorizing different political ideologies based on their stances on social and economic issues. By visually representing these ideologies, students can gain a deeper understanding of the diverse range of political beliefs present in society.
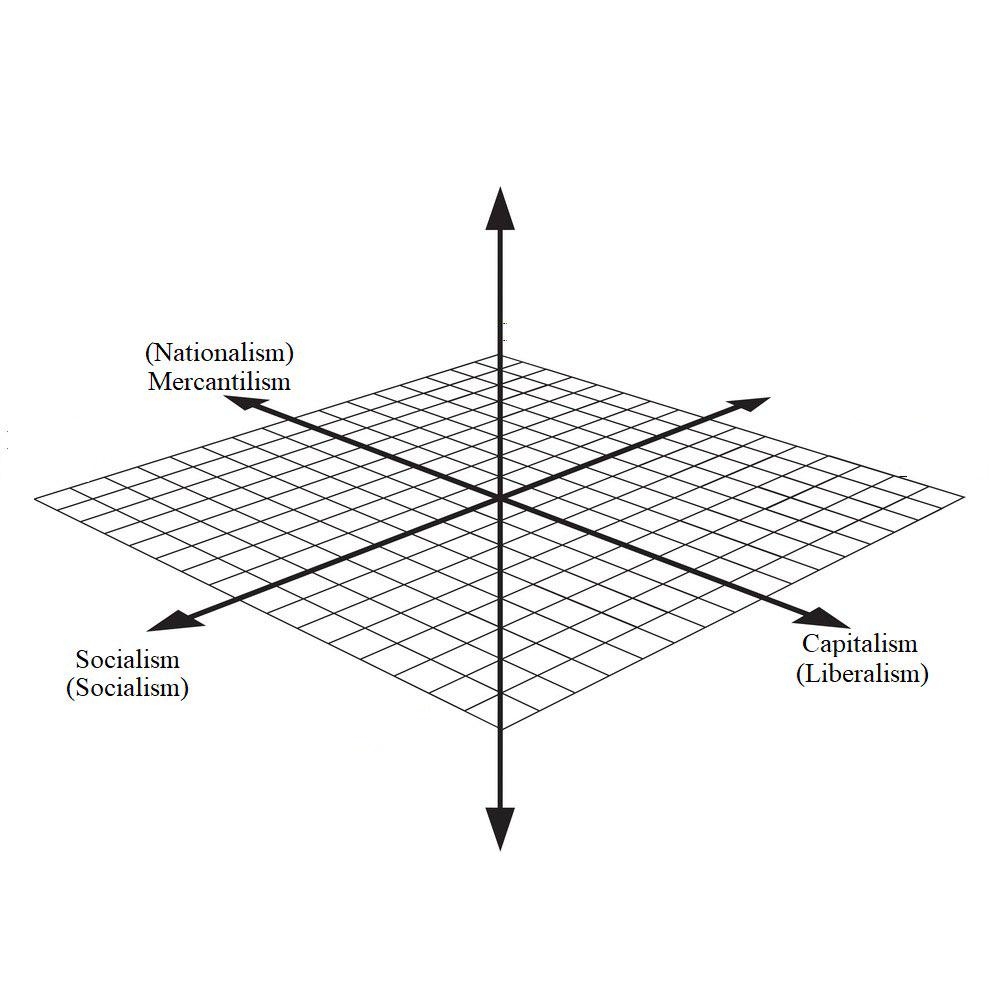
Thoughts On My 3 dimensional Political Compass R PoliticalDebate
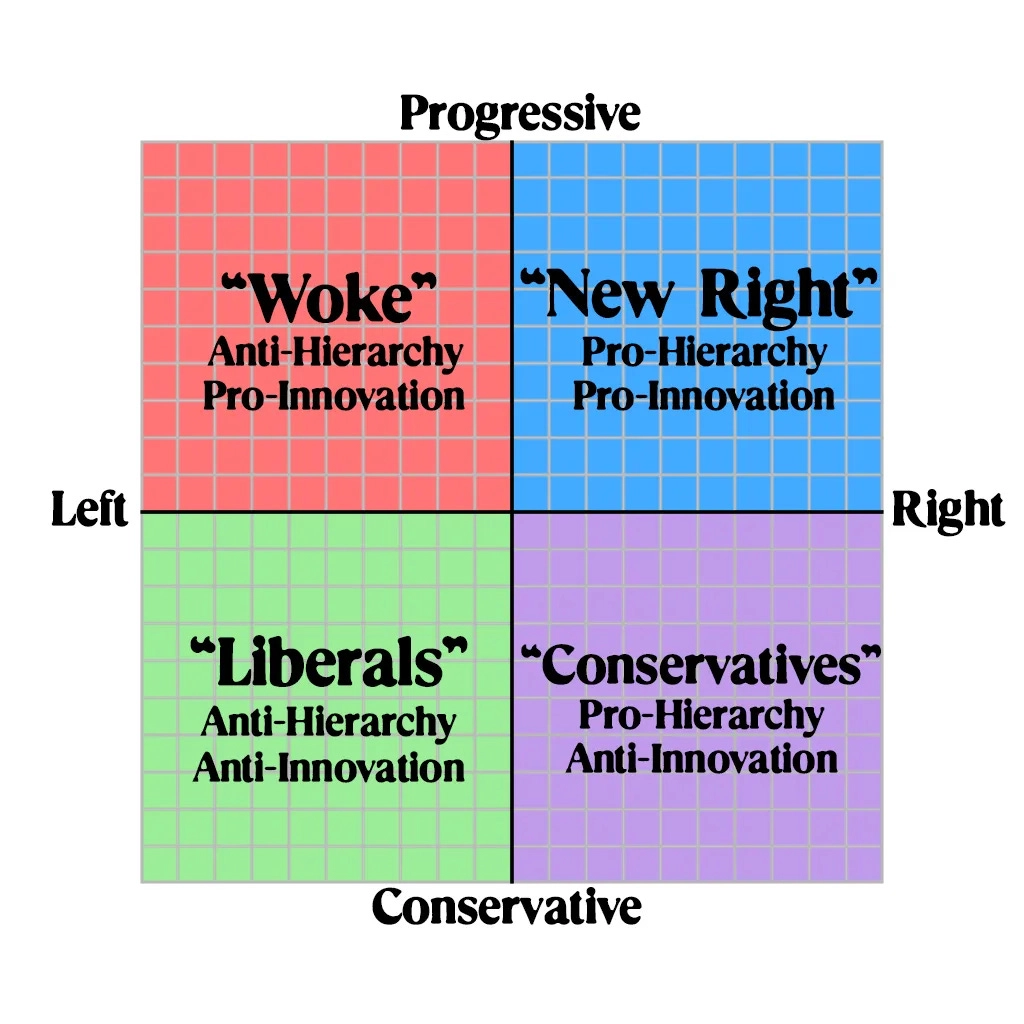
A New Political Map By Phillip Johnston And Andy Patton