Understanding the different quadrants in a graph can be a bit tricky at first, but once you get the hang of it, it’s actually quite simple. Graphs are used to visually represent data points and relationships between them.
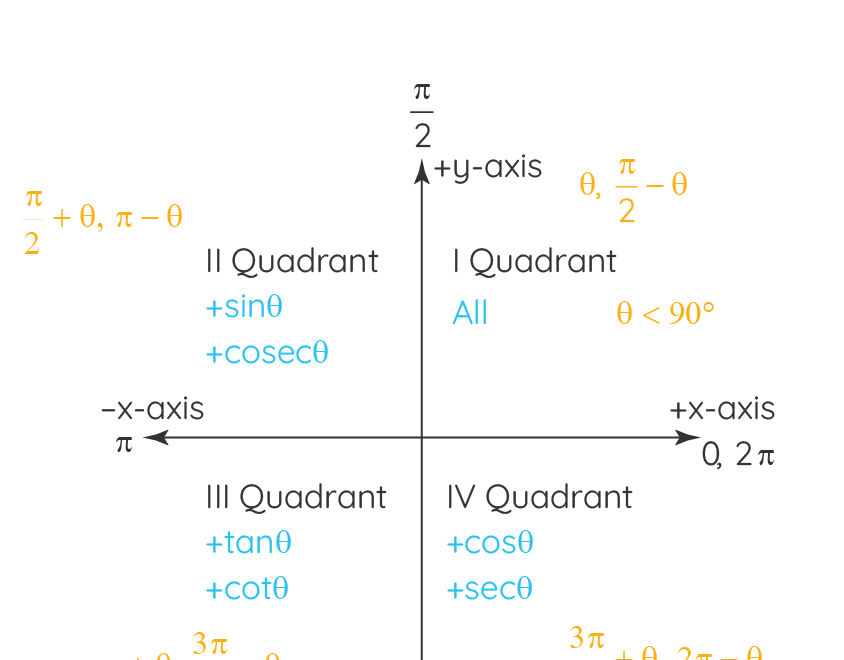
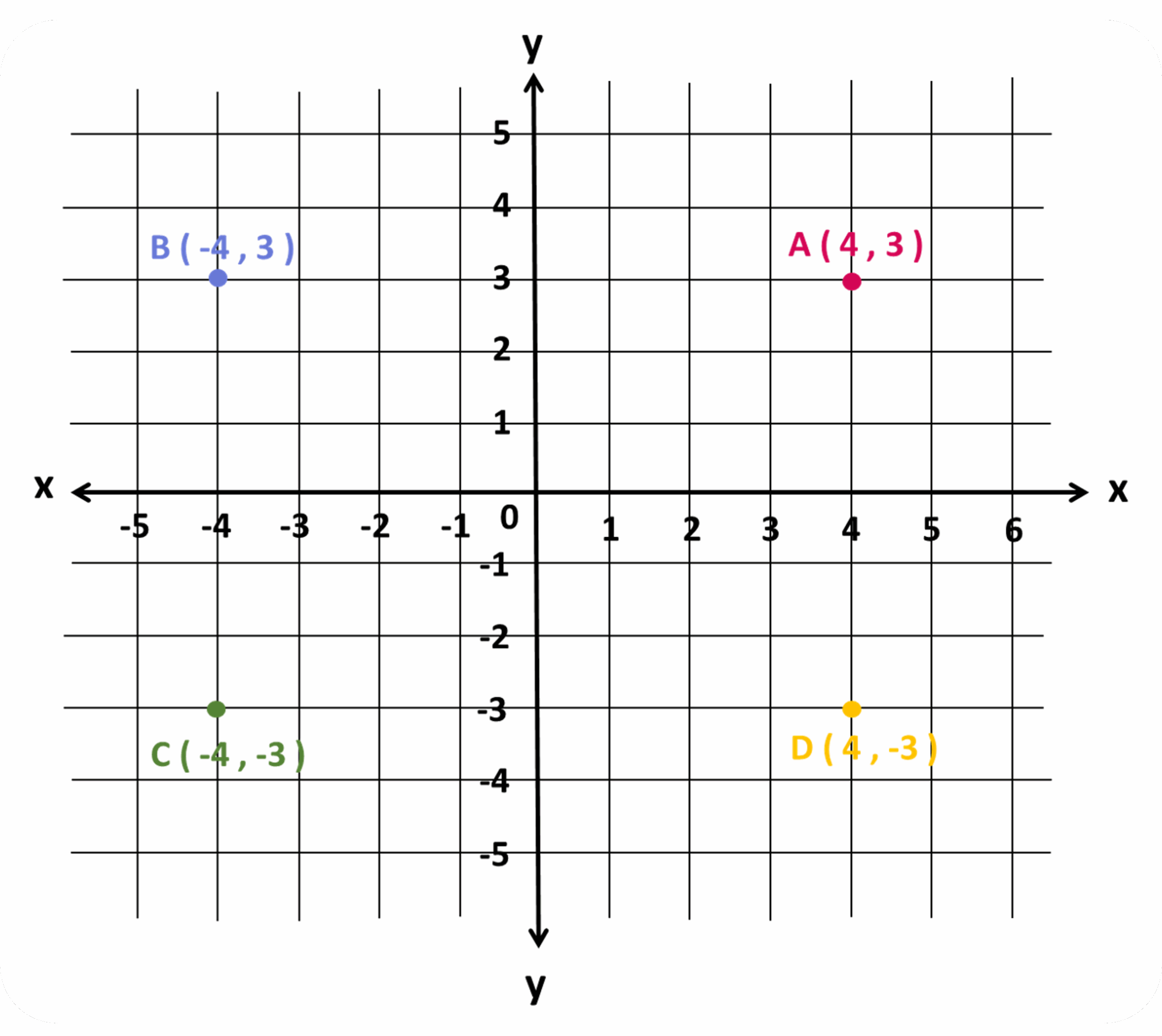
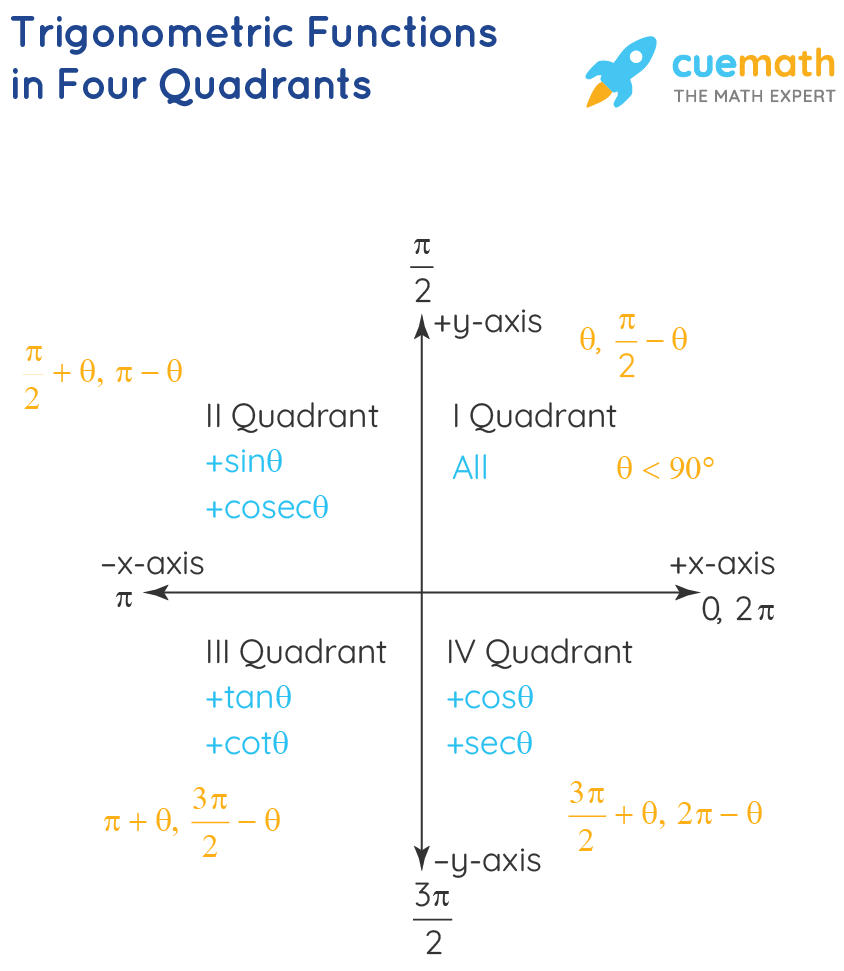
Each quadrant in a graph is defined by the signs of the x and y coordinates. Quadrant I is in the top right, Quadrant II in the top left, Quadrant III in the bottom left, and Quadrant IV in the bottom right.
Different Quadrants In Graph
Different Quadrants In Graph
Quadrant I is where both x and y values are positive. Quadrant II is where x is negative and y is positive. Quadrant III is where both x and y are negative, and Quadrant IV is where x is positive and y is negative.
When plotting points on a graph, it’s important to pay attention to which quadrant they fall into. This helps in understanding the relationship between variables and making accurate interpretations of the data presented.
Whether you’re studying mathematics, economics, or any other field that involves graphs, knowing the different quadrants and how to interpret them will be valuable. It’s a fundamental concept that lays the groundwork for more complex analyses.
So next time you come across a graph, take a moment to identify the quadrants and see how the data points are distributed. It’s a great way to enhance your graph-reading skills and gain a deeper understanding of the information being presented.
04 Negative Numbers And The Coordinate Plane Eduki
Trigonometric Functions Formulas Graphs Examples Values