Are you struggling to understand the concept of plain graphs in the first and second quadrants? Don’t worry, we’ve got you covered! Plain graphs can be a bit tricky at first, but once you get the hang of it, you’ll see how useful they can be.
Plain graphs are essential in mathematics and are used to represent data visually. They consist of two axes – the x-axis and the y-axis. The x-axis runs horizontally, while the y-axis runs vertically. The point where the two axes intersect is called the origin.
Plain Graph First And Second Quadrant
Plain Graph First And Second Quadrant
In the first quadrant, both the x and y values are positive. This means that all the points in this quadrant have positive coordinates. As you move counterclockwise around the origin, you enter the second quadrant, where the x values are negative, but the y values remain positive.
Understanding plain graphs in the first and second quadrants is crucial for solving mathematical problems and analyzing data. By plotting points on a graph, you can easily visualize relationships between variables and identify patterns that may not be apparent from raw data alone.
Whether you’re studying algebra, geometry, or any other branch of mathematics, mastering plain graphs is a fundamental skill that will serve you well in your academic and professional pursuits. So don’t be intimidated by them – embrace them as powerful tools to help you make sense of the world around you.
Next time you come across a plain graph in the first and second quadrants, remember that it’s just a visual representation of data that can help you gain insights and solve problems more effectively. With a bit of practice, you’ll soon become a pro at interpreting and using plain graphs to your advantage!
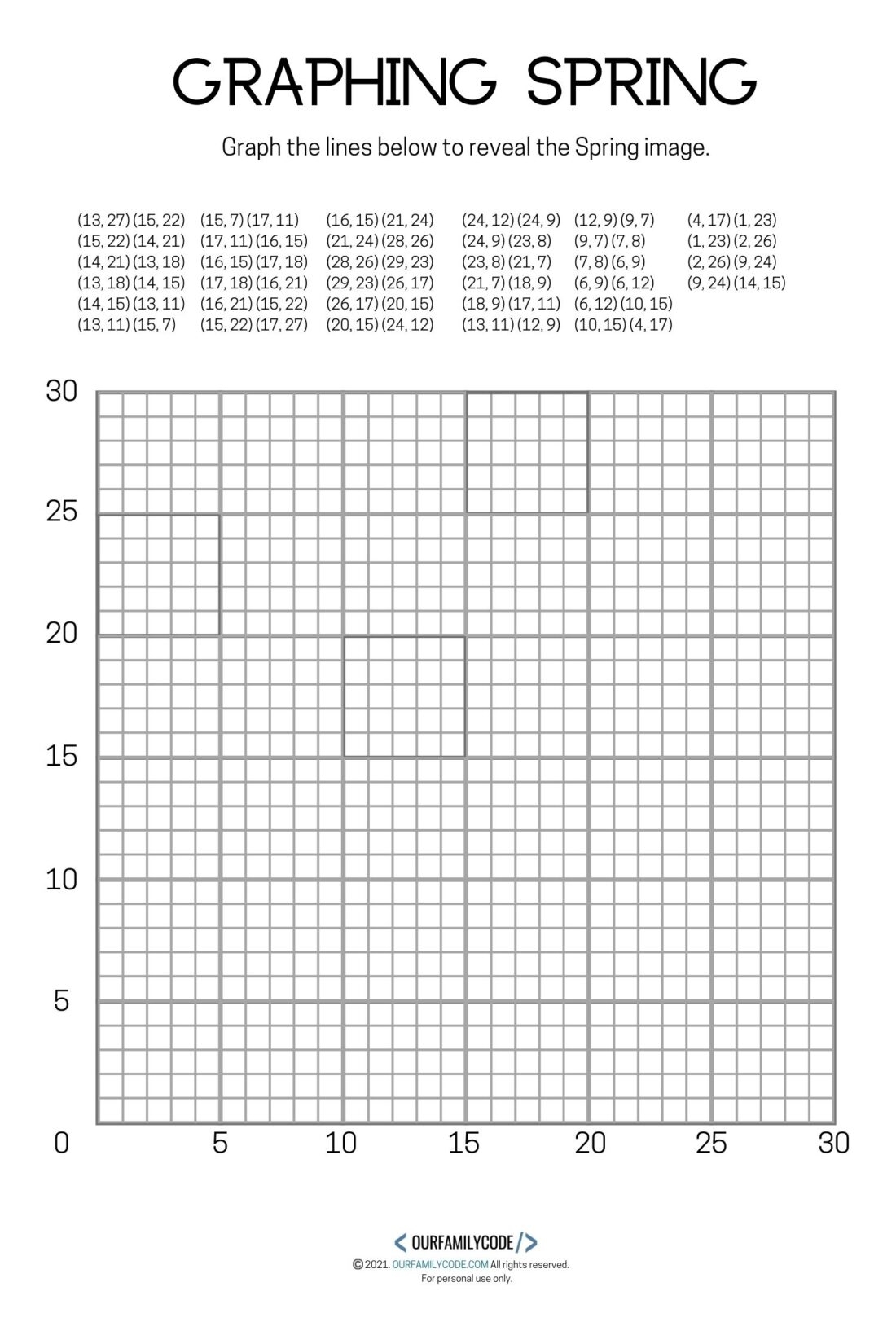
4 Free Spring Graphing Coordinate Plane Worksheets Our Family Code
Coordinate Plane Grid Worksheets Library