If you’ve ever struggled with understanding polar coordinate graph radians, fear not! This article is here to demystify this topic for you. Polar coordinates are a way to locate points in a plane using distance and angle measurements.
When we talk about radians in a polar coordinate graph, we are referring to the angle measurement used to locate a point. Radians are a unit of measurement for angles, with one full rotation around a circle equaling 2π radians.
Polar Coordinate Graph Radians
Understanding Polar Coordinate Graph Radians
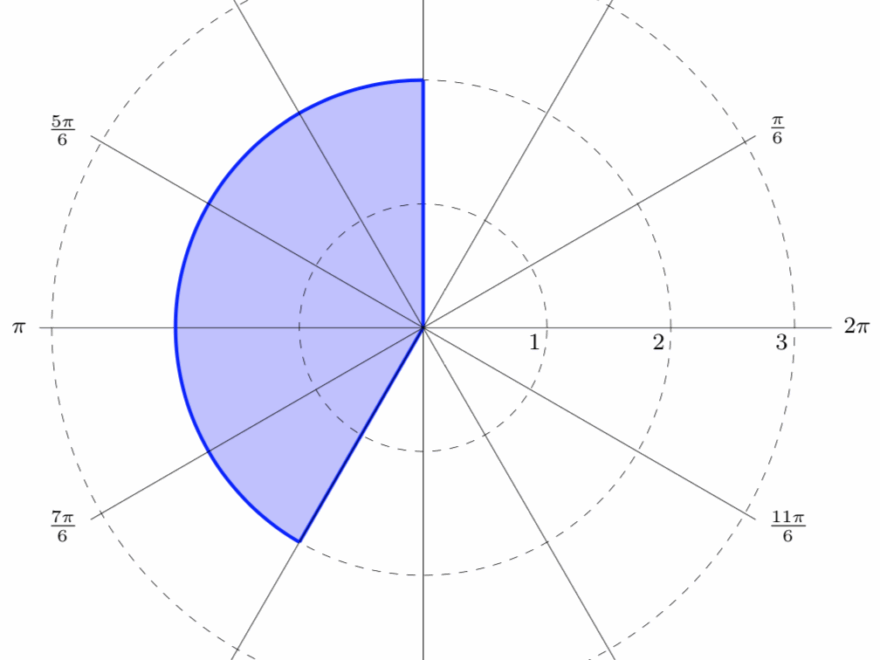
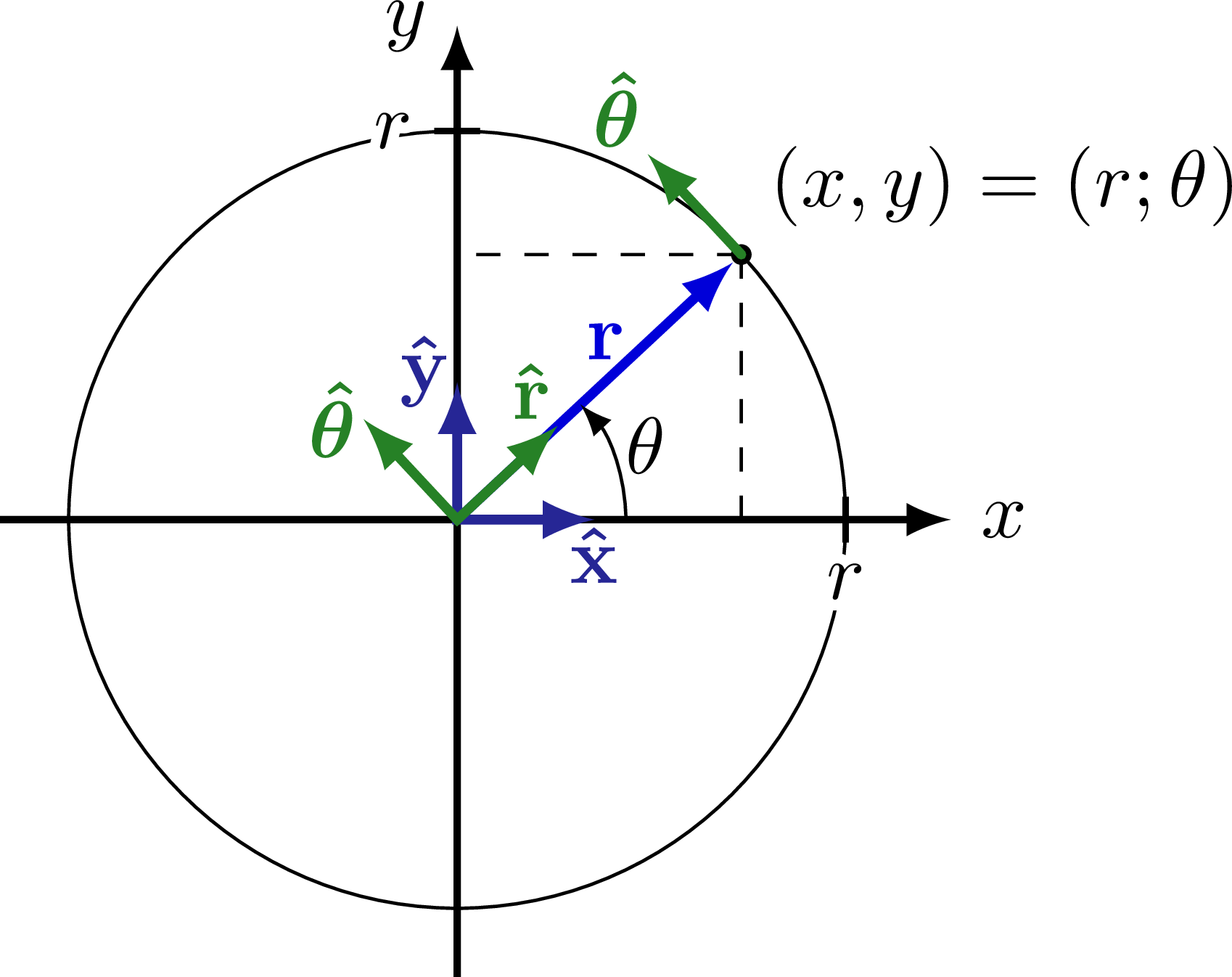
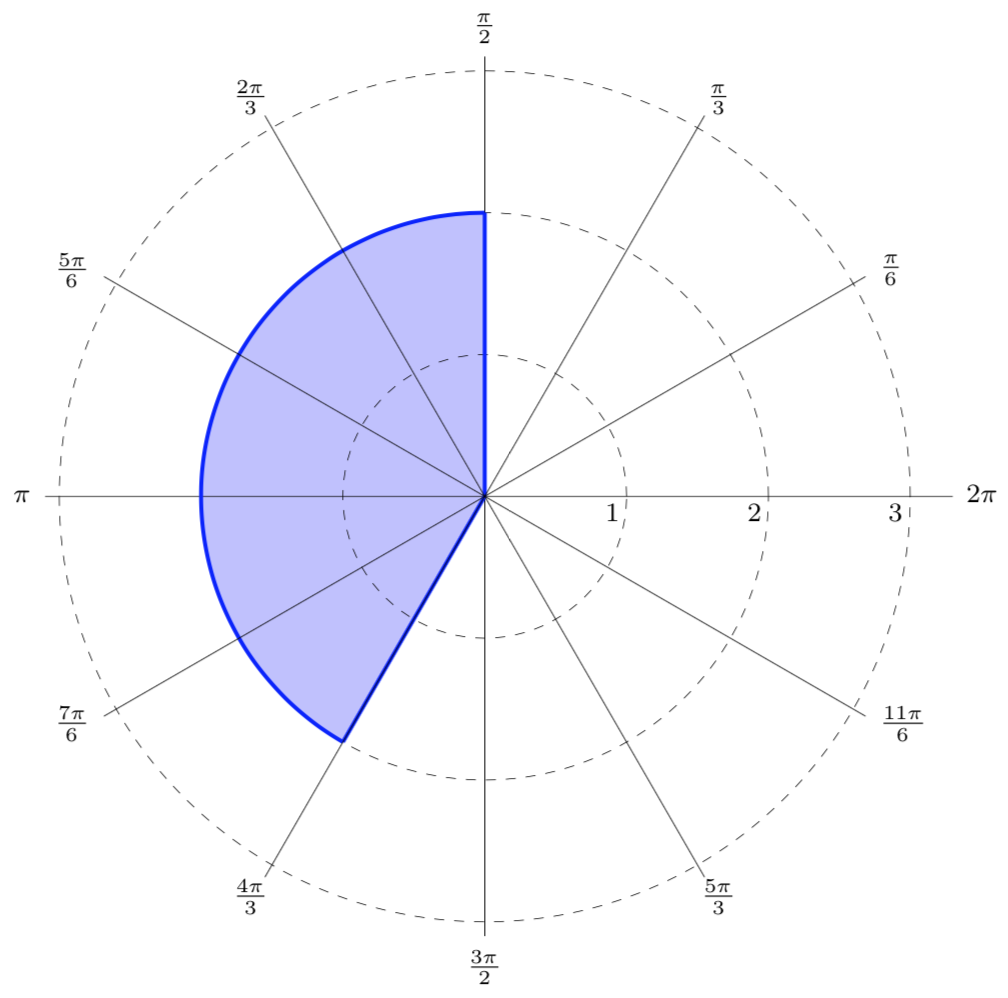
In a polar coordinate system, points are located by their distance from the origin (r) and the angle they make with the positive x-axis (θ). Radians are used to measure this angle, with 0 radians pointing to the right along the x-axis.
As you move counterclockwise around the origin, the angle measurement increases. One full rotation around the origin equals 2π radians, which is equivalent to 360 degrees in a Cartesian coordinate system.
Graphing in polar coordinates can create beautiful and intricate patterns, such as spirals, circles, and cardioids. By understanding how radians work in this system, you can accurately plot points and create stunning visual representations of mathematical functions.
So, the next time you come across a polar coordinate graph radians problem, remember that radians are simply a way to measure angles in a polar coordinate system. With a bit of practice and understanding, you’ll be navigating these graphs with ease!
In conclusion, polar coordinate graph radians may seem daunting at first, but with a little practice and patience, you’ll soon master this concept. Remember, radians are just a different way to measure angles, and once you grasp the basics, you’ll be graphing in polar coordinates like a pro!
Polar Coordinates Radians TikZ
MFG Polar Coordinates