Have you ever heard of polar coordinates before? They’re a unique way of graphing points on a plane that uses angles and distances instead of x and y coordinates. It might sound complicated at first, but once you get the hang of it, it’s actually quite simple and can be really fun to work with!
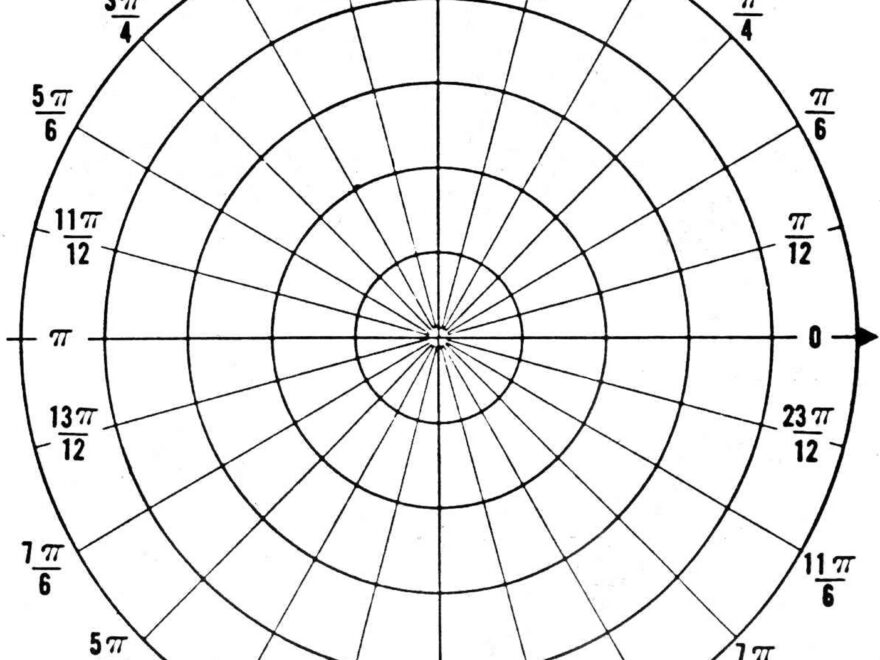
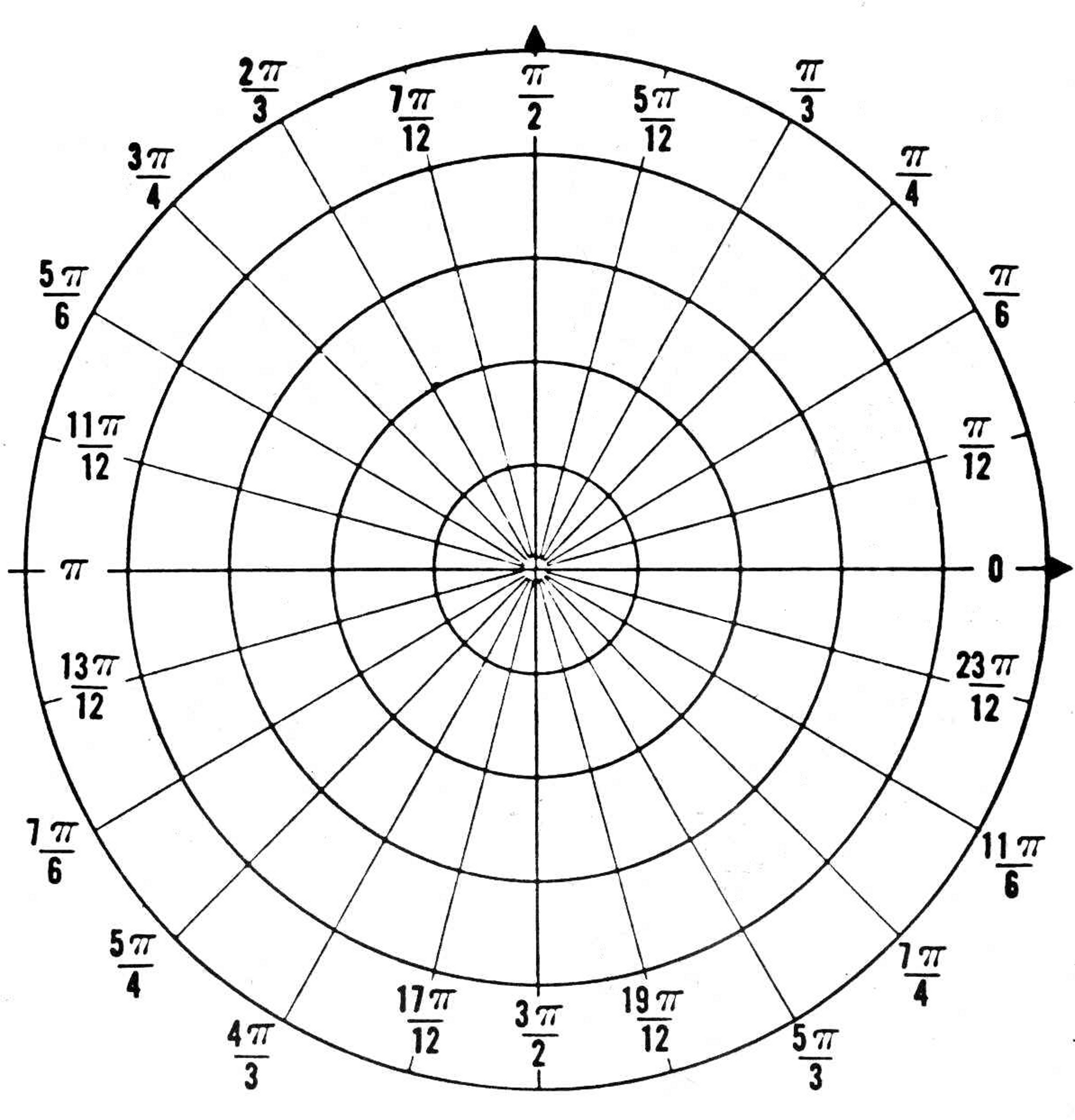
With polar coordinates, you use an angle (usually denoted by theta) and a distance from the origin (usually denoted by r) to pinpoint a specific point on a graph. This method is especially useful when dealing with circular or radial patterns, making it a valuable tool in various fields such as physics, engineering, and even art.
Polar Coordinates Graph 1 2
Polar Coordinates Graph 1 2
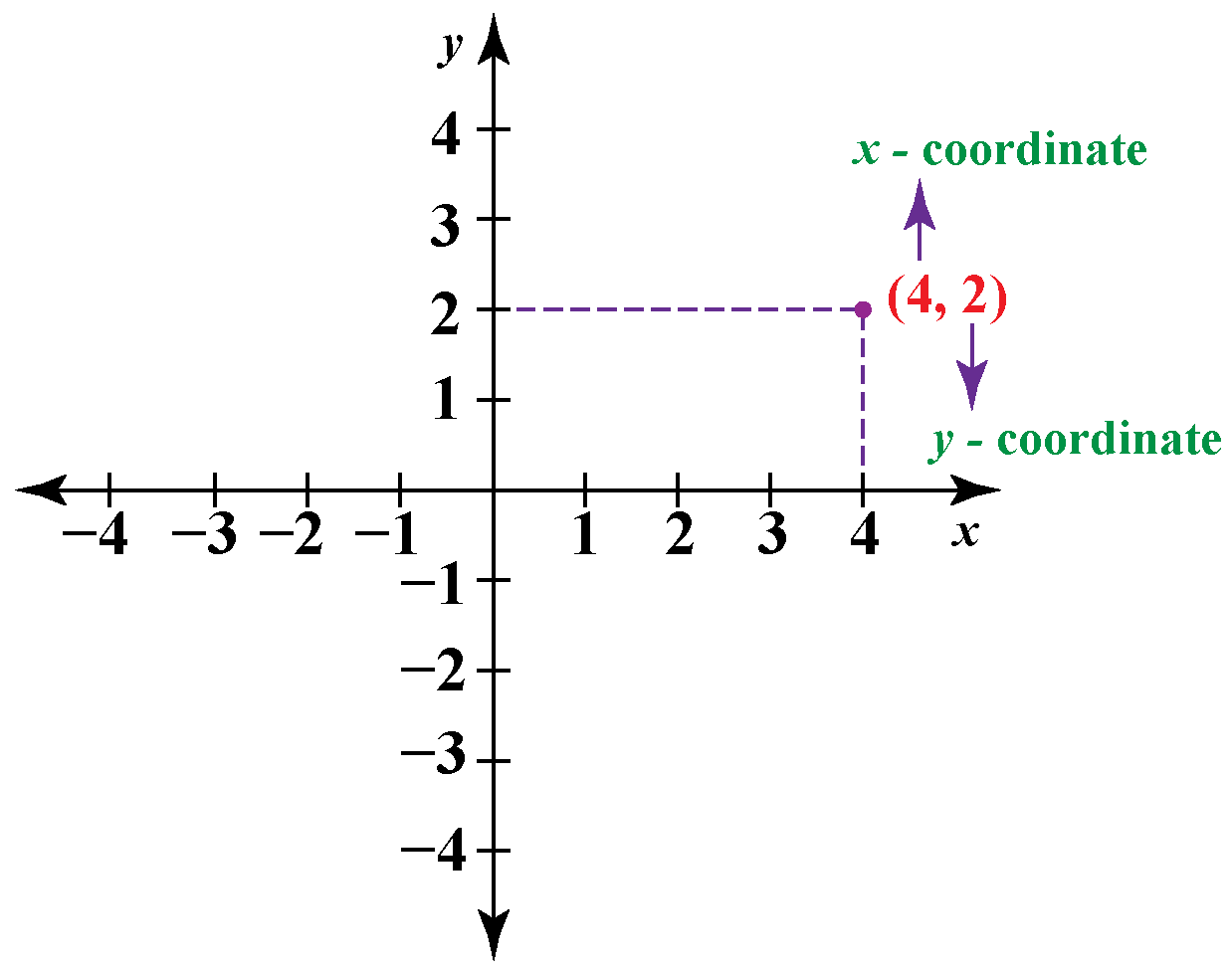
When graphing in polar coordinates, the angle theta is measured counterclockwise from the positive x-axis, and the distance r represents how far away the point is from the origin. To plot a point in polar coordinates (r, theta), you first move r units away from the origin at the angle theta.
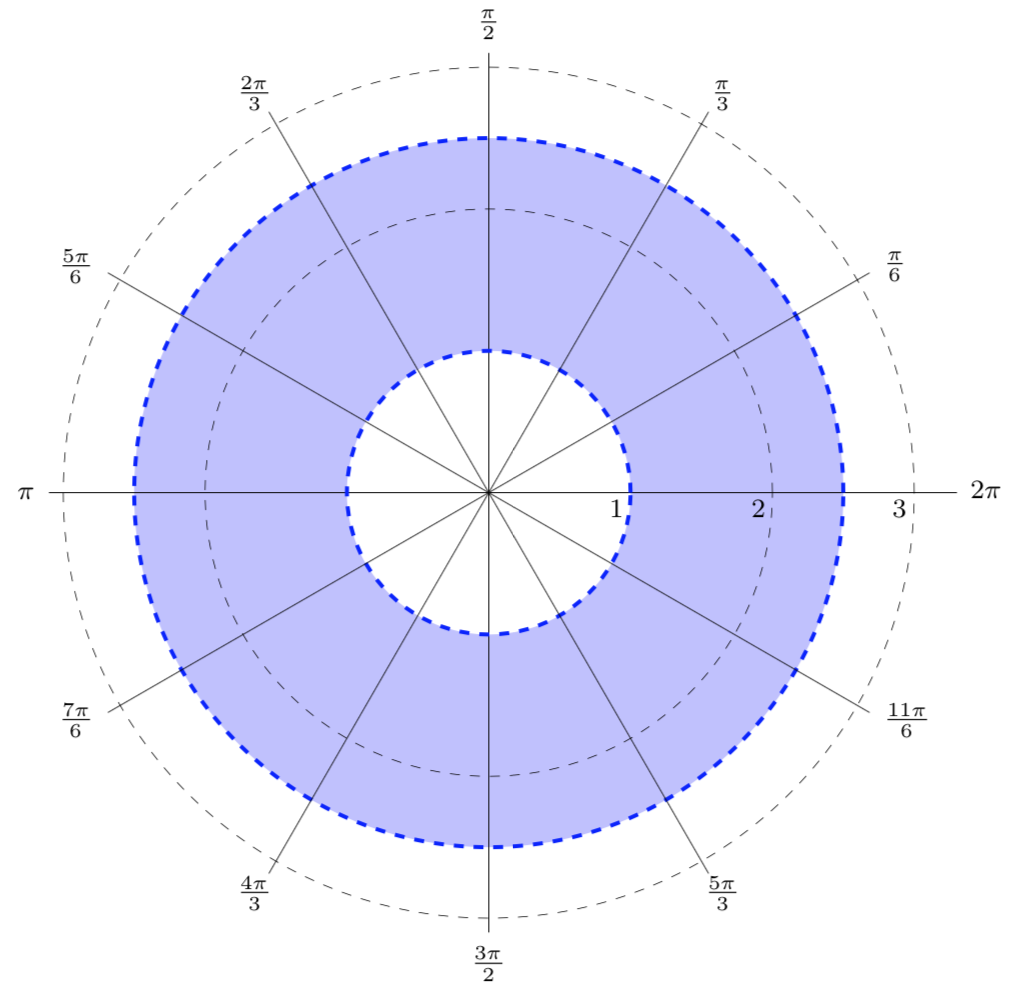
One common example of using polar coordinates is graphing circles. The equation for a circle centered at the origin with radius r is simply r = constant. This means that all points on the circle are equidistant from the origin, making it easy to visualize using polar coordinates.
Another interesting application of polar coordinates is graphing spirals. By adjusting the angle and distance values, you can create beautiful spiral patterns that are both aesthetically pleasing and mathematically intriguing. It’s a great way to explore the relationship between geometry and algebra in a new light.
Overall, polar coordinates offer a fresh perspective on graphing that can be both practical and creative. Whether you’re studying math, science, or just looking to try something new, learning how to work with polar coordinates can open up a world of possibilities. So grab a pencil, some graph paper, and start exploring the fascinating realm of polar graphs!
MFG Polar Coordinates
Polar Coordinates A Minimum Of Blind Calculation